The Greenhouse Effect and our Planet
Table Of Content
In general, smog is generally formed by the accumulation of more greenhouse gases including nitrogen and sulfur oxides. The major contributors to the formation of smog are automobile and industrial emissions, agricultural fires, natural forest fires and the reaction of these chemicals among themselves. The major cause of this phenomenon is the accumulation of natural greenhouse gases including chlorofluorocarbons, carbon dioxide, methane, etc.
Greenhouse gases and climate change
"Deforestation is the second largest anthropogenic source of carbon dioxide to the atmosphere ranging between 6 percent and 17 percent," said Daley. Humans directly affect the greenhouse effect through activities that result in greenhouse gas emissions. The Earth system model below includes some of the ways that human activities increase the amount of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere.
How are humans impacting the greenhouse effect?
The Greenhouse Effect and our Planet - National Geographic Society
The Greenhouse Effect and our Planet.
Posted: Thu, 19 Oct 2023 07:00:00 GMT [source]
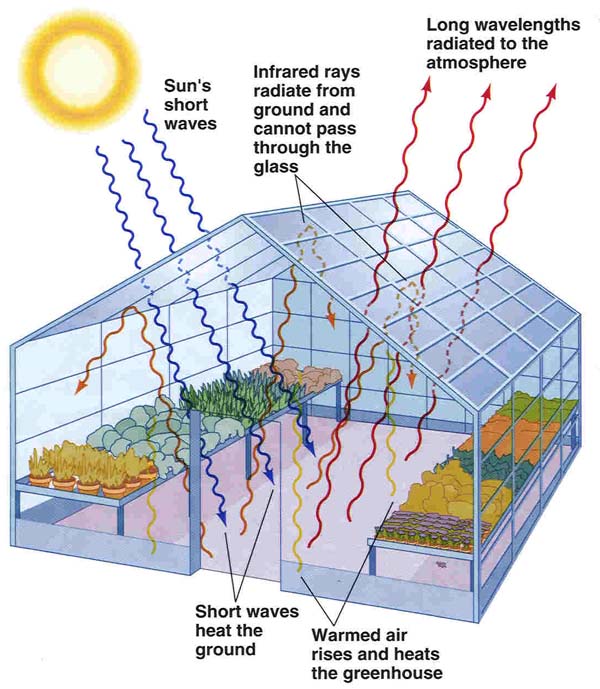
Surface heating can happen from an internal heat source as in the case of Jupiter, or from its host star as in the case of the Earth. In the case of Earth, the Sun emits shortwave radiation (sunlight) that passes through greenhouse gases to heat the Earth's surface. In response, the Earth's surface emits longwave radiation that is mostly absorbed by greenhouse gases. The absorption of longwave radiation prevents it from reaching space, reducing the rate at which the Earth can cool off.
What Are the Causes of Climate Change?
Although Yousaf on Monday acknowledged his mistake, it was too late to repair the damage. But the SNP's focus will be on selecting a leader who can repair the party's image in Scotland and attract support from at least one opposition party in the regional parliament, where it is one seat short of a majority with 63 of the 128 voting seats. The industries and factories produce harmful gases which are released in the atmosphere. If there were no greenhouse effect on Earth, our planet would probably look a lot like Mars. Mars doesn't have a thick enough atmosphere to reflect much heat back to the planet, so it gets very cold there.
What Is the Greenhouse Effect? Is It Inherently Bad?
This is about 15 °C (59 °F),[4][44] a bit lower than the effective surface temperature. This value is 33 °C (59 °F) warmer than Earth's overall effective temperature. Burning fossil fuels like coal and oil puts more carbon dioxide into our atmosphere. Fourier, however, neither used the term greenhouse effect nor credited atmospheric gases with keeping Earth warm. Swedish physicist and physical chemist Svante Arrhenius is credited with the origins of the term in 1896, with the publication of the first plausible climate model that explained how gases in Earth’s atmosphere trap heat. Arrhenius first refers to this “hot-house theory” of the atmosphere—which would be known later as the greenhouse effect—in his work Worlds in the Making (1903).
From the beginning of the Industrial Revolution through the end of the 20th century, the amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere increased by roughly 30 percent and the amount of methane more than doubled. This global warming could alter Earth’s climates and thereby produce new patterns and extremes of drought and rainfall and possibly disrupt food production in certain regions. From the beginning of the Industrial Revolution through the end of the 20th century, the amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere increased by roughly 30 percent and the amount of methane more than doubled. This global warming could alter Earth’s climates and thereby produce new patterns and extremes of drought and rainfall and possibly disrupt food production in certain regions. It is the phenomenon of a gradual increase in the average temperature of the Earth’s atmosphere. The main cause for this environmental issue is the increased volumes of greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide and methane released by the burning of fossil fuels, emissions from the vehicles, industries and other human activities.
Search

But in recent history, human activity is throwing off the balance of greenhouse gases. To get energy or electricity, we burn fossil fuels like coal, oil, and natural gas. This releases carbon dioxide and other greenhouses gases into the atmosphere. The more greenhouses gases we put into the atmosphere, the more heat they absorb—and the warmer our Earth becomes. The presence of "greenhouse" gases in the atmosphere, however, changes the radiation balance.
Climate Change Indicators: Atmospheric Concentrations of Greenhouse Gases US EPA - U.S. EPA.gov
Climate Change Indicators: Atmospheric Concentrations of Greenhouse Gases US EPA.
Posted: Wed, 01 Nov 2023 07:00:00 GMT [source]
Halting the trends in motion will require more than just phasing out fossil fuels. In fact, the paths to halting global temperature increases of 1.5 or 2 degrees C, the two goals outlined by the IPCC, rely in some way on adopting methods of sucking CO2 from the sky. Those include planting trees, conserving existing forests and grasslands, and capturing CO2 from power plants and factories. By trapping heat from the sun, greenhouse gases have kept Earth's climate habitable for humans and millions of other species. But those gases are now out of balance and threaten to change drastically which living things can survive on this planet—and where. Increases in greenhouse gases in the coming decades are expected to harm human health, increase droughts, contribute to sea level rise, and decrease national security and economic well-being throughout the world.

But some of the heat is trapped by the greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. That's what keeps our Earth a warm and cozy 58 degrees Fahrenheit (14 degrees Celsius), on average. Energy emitted from the sun ("solar radiation") is concentrated in a region of short wavelengths including visible light.
But overhauling our energy systems will require transformative, aggressive global action—right now. According to the IPCC, we must halve greenhouse gas pollution by 2030 and reach net-zero emissions by 2050. Climate change impacts where we can live, how we work, how we grow our food—especially if we live or work in frontline communities. Warmer temperatures mean more insects that spread diseases like dengue fever—and heat waves are getting hotter and becoming more lethal to humans.
Rising sea levels cause flooding in coastal cities, which could displace millions of people in low-lying areas such as Bangladesh, the U.S. state of Florida, and the Netherlands. According to scientists, the average temperature of Earth would drop from 14˚C (57˚F) to as low as –18˚C (–0.4˚F), without the greenhouse effect. A simple picture assumes a steady state, but in the real world, the day/night (diurnal) cycle, as well as the seasonal cycle and weather disturbances, complicate matters. At night the atmosphere cools somewhat, but not greatly because the thermal inertia of the climate system resists changes both day and night, as well as for longer periods.[53] Diurnal temperature changes decrease with height in the atmosphere. Just like a glass greenhouse, Earth's greenhouse is also full of plants!
Comments
Post a Comment